About Cornerstone Fair Value Model
For over 30 years, Cornerstone’s Fair Value Model has performed a weekly appraisal for the value of each of the 800 companies that we cover in the large-cap universe. By identifying companies with consistent and predictable earnings streams as well as applying an appropriate multiple to companies based on their financial and operating leverage, the Cornerstone Fair Value Model has been able to identify those companies with a greater chance to outperform. History has demonstrated that an attractive relative valuation has been a key determinant of outperforming companies.
As illustrated in the chart below, those companies that fall within the first quintile (most attractive stocks) have outperformed the S&P 500, as well as the least attractive companies in the fifth quintile by a significant margin since its creation in 1987. Read on for a more complete description of how cornerstones fair value model operates, or contact us directly for more details.
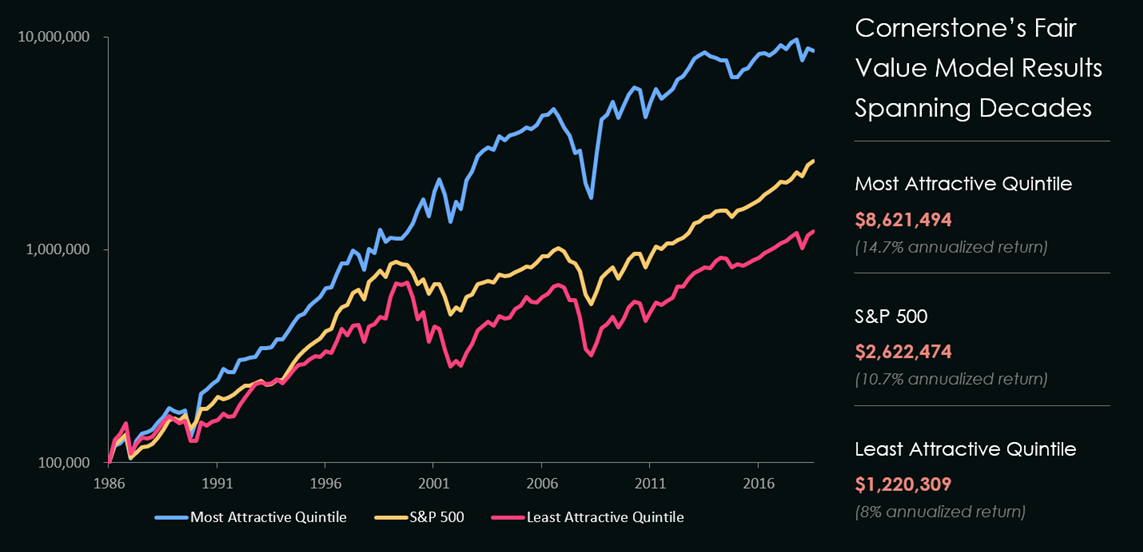
Cornerstone’s Fair Value Model not only identifies stocks that appear attractive, but allows users to explore why the stock appears undervalued. The focus of the model helps you direct further research into the factors that determine the Fair Value: profitability, earnings power, leverage, payout policies, etc. Our 800 stock universe is re-ranked weekly to incorporate all price changes, earnings reports, and analyst estimate changes, and establishes a fair price for each stock in our universe.
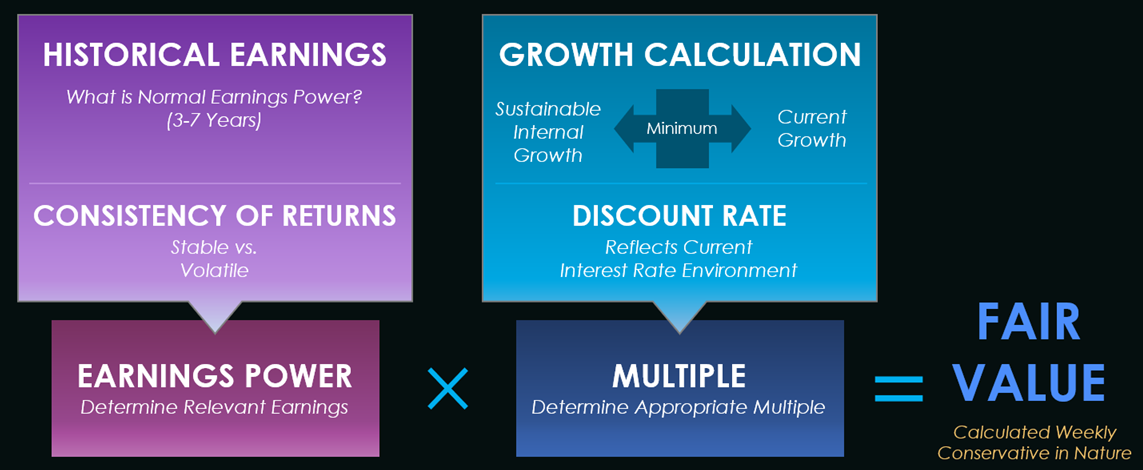
This value is based on two factors:
- The normalized earnings power of that company.
- The multiple placed on the company’s normalized earnings power
See the schematic below for a simplified illustration of how the Fair Value Model works.
Past performance is not indicative of future results.
The Fair Value Model is Cornerstone's proprietary tool which aims to identify companies with a greater chance to outperform. These companies are ranked using Cornerstone's Fair Value Methodology.